Male fertility hinges on robust sperm health, yet modern lifestyles often compromise reproductive capacity. The encouraging reality is that spermatogenesis—the complete cycle of sperm cell development—takes approximately 90 days, providing a clear window for targeted interventions to improve sperm quality.
This comprehensive guide delivers actionable strategies for busy adults seeking to enhance fertility parameters, including motility, morphology, and concentration.
Whether you’re planning parenthood or optimizing reproductive wellness, these evidence-based weekly habits transform sperm health without overwhelming your schedule.
Understanding how to improve sperm quality requires a commitment to nutritional precision, lifestyle modifications, and the consistent implementation of scientifically validated practices that support spermatogenic function.
Understanding Sperm Quality Fundamentals
What Defines Healthy Sperm
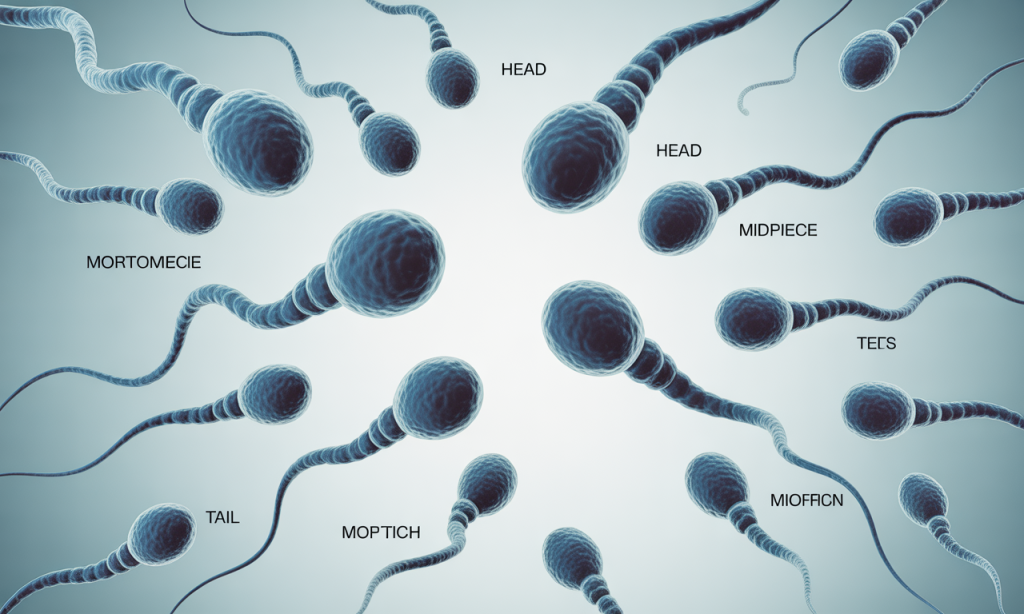
Sperm quality encompasses multiple parameters that fertility specialists assess during semen analysis. Concentration refers to the number of spermatozoa per milliliter; normal values exceed 15 million per milliliter according to World Health Organization standards.
Motility measures the percentage of sperm demonstrating progressive movement, ideally above 40% for optimal fertilization potential.
Morphology evaluates structural integrity, examining head shape, midpiece configuration, and tail formation. Healthy sperm exhibit oval heads and intact acrosomes containing enzymes necessary for oocyte penetration.
DNA fragmentation index represents another critical marker, measuring chromosomal damage that impairs embryonic development even when other parameters appear normal.
The 90-Day Regeneration Cycle
Spermatogenesis unfolds across approximately 74 days, with an additional 14-21 days required for epididymal maturation. This biological timeline means that today’s lifestyle choices directly influence sperm quality three months from now. Testicular seminiferous tubules house spermatogonial stem cells that undergo mitotic and meiotic divisions, ultimately giving rise to mature spermatozoa.
Environmental exposures, nutritional deficiencies, and oxidative stress during this developmental window permanently affect sperm cohort quality. Consequently, the 90-day intervention period provides sufficient duration to observe measurable improvements in semen parameters. Clinical studies demonstrate significant enhancements in motility, concentration, and DNA integrity following three-month lifestyle modification protocols.
Common Quality Impairments
Asthenozoospermia describes reduced sperm motility affecting fertilization capability. Contributing factors include mitochondrial dysfunction, structural defects, and oxidative damage to flagellar proteins. Teratozoospermia indicates abnormal sperm morphology, often resulting from disrupted spermatogenesis caused by hormonal imbalances or genetic factors.
Oligozoospermia refers to low sperm concentration, frequently linked to varicoceles, hormonal disorders, or testicular heat exposure. DNA fragmentation is an increasingly recognized pathology in which chromosomal breaks compromise genetic integrity despite otherwise normal semen parameters. Identifying specific impairments enables targeted intervention strategies for optimal results.
Nutritional Architecture for Sperm Enhancement
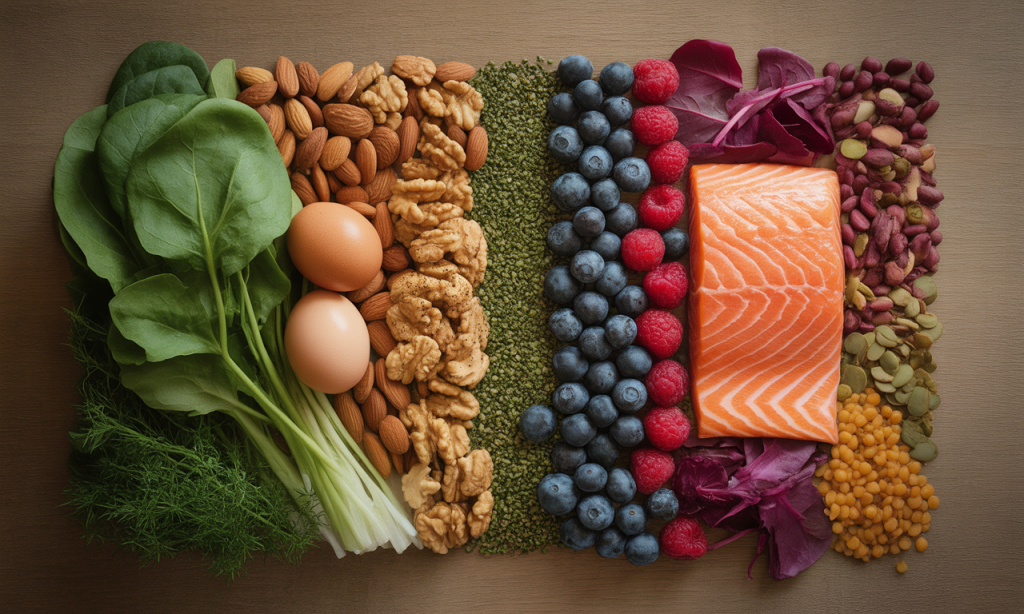
Antioxidant-Rich Dietary Framework
Reactive oxygen species inflict substantial damage to sperm membranes and DNA during spermatogenesis. Antioxidants neutralize these harmful molecules, preserving cellular integrity throughout the 90-day maturation cycle. Vitamin C concentrations in seminal plasma directly correlate with sperm motility and DNA protection, with recommended intake reaching 200-1000mg daily from dietary sources.
Vitamin E functions synergistically with vitamin C, safeguarding polyunsaturated fatty acids in sperm membranes from peroxidation. Alpha-tocopherol supplementation has been shown to improve fertilization rates in clinical trials. Selenium supports glutathione peroxidase activity, a critical enzymatic defense system against oxidative stress in developing spermatozoa.
Essential antioxidant sources include:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, blackberries) containing anthocyanins
- Citrus fruits provide ascorbic acid and bioflavonoids
- Nuts and seeds are rich in vitamin E and selenium
- Dark leafy greens offer multiple phytonutrients
- Tomatoes containing lycopene for prostate health
Micronutrient Optimization Protocol
Zinc plays an indispensable role in testosterone synthesis, the regulation of spermatogenesis, and the stabilization of sperm membranes. Deficiency correlates with oligozoospermia and hypogonadism, while supplementation improves concentration and motility. Oysters provide exceptional zinc bioavailability, though beef, poultry, and pumpkin seeds offer practical alternatives for daily consumption.
Folate participates in DNA synthesis and methylation processes crucial during rapid cell division in seminiferous tubules. Low folate status is associated with increased DNA fragmentation and chromosomal abnormalities. Dark leafy vegetables, legumes, and fortified grains supply adequate folate when consumed consistently throughout the intervention period.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), comprise significant portions of sperm membrane phospholipids. These essential fats enhance membrane fluidity, supporting proper flagellar function and acrosomal reactions. Consuming fatty fish twice weekly or taking algae-based supplements for plant-based individuals ensures sufficient omega-3 intake.

Hydration and Seminal Volume
Adequate hydration maintains seminal plasma volume and optimal sperm concentration ratios. Dehydration reduces ejaculate volume and increases seminal viscosity, potentially impeding sperm motility. Target consumption of 3-4 liters daily, adjusting for activity level, climate, and body mass.
Water quality matters significantly, as contaminants, including heavy metals and endocrine disruptors, concentrate in reproductive tissues. Filtered water minimizes exposure to chlorine, fluoride, and pharmaceutical residues that may interfere with hormonal signaling. Herbal teas provide additional hydration with phytonutrient benefits, though excessive caffeine requires moderation.
Foods and Substances to Eliminate
Processed meats containing nitrates and nitrites generate oxidative stress and DNA damage in developing sperm cells. Trans fats found in fried foods and commercial baked goods disrupt cellular membrane composition and hormonal balance. High-glycemic refined carbohydrates trigger insulin spikes that suppress testosterone production and promote inflammation.
Alcohol consumption exceeding moderate levels—two drinks daily—significantly impairs spermatogenesis through multiple mechanisms. Ethanol metabolites damage Sertoli cells, which nurture developing spermatocytes, while acetaldehyde directly harms DNA integrity. Soy products in excessive quantities may influence estrogen receptor activity, though moderate consumption in whole-food contexts appears benign.
Eliminate or minimize:
- Processed meats (bacon, sausage, deli meats)
- Deep-fried foods and commercial baked goods
- Sugar-sweetened beverages and refined carbohydrates
- Excessive alcohol consumption beyond one drink per day
- Foods containing artificial additives and preservatives
Weekly Habit Implementation Blueprint
Weeks 1-4: Foundation Phase
The inaugural month establishes foundational habits without overwhelming existing schedules. Week one prioritizes dietary assessment, eliminating processed foods and incorporating five servings of vegetables daily. Document baseline eating patterns to identify opportunities for improvement and track compliance throughout the intervention.
Week two introduces strategic supplementation, including multivitamins, omega-3s, and antioxidant formulations. Morning implementation ensures consistency and optimal absorption with food. Begin twice-weekly strength-training sessions targeting major muscle groups, stimulating testosterone production with compound movements.
Week three adds stress management practices, dedicating 10 minutes daily to mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises. Cortisol elevation suppresses gonadotropin-releasing hormone, disrupting the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Replace evening screen time with relaxation routines supporting circadian rhythm optimization.
Week four incorporates sleep hygiene protocols, establishing consistent bedtimes and wake times even on weekends. Darkness, cool temperatures (65-68°F), and the removal of electronic devices enhance sleep architecture. Growth hormone and testosterone secretion peak during deep sleep stages, making quality rest non-negotiable for reproductive optimization.
Weekly checklist items:
- Meal prep Sunday for weekday nutrition compliance
- Schedule three 30-minute exercise sessions
- Take supplements with breakfast and dinner
- Practice a 10-minute stress reduction technique daily
- Maintain a consistent sleep-wake schedule
- Track water intake reaching 3+ liters
- Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and recreational substances
Weeks 5-8: Intensification Phase

Progressive overload principles apply to exercise programming during month two. Increase resistance training frequency to 3 sessions per week, emphasizing squats, deadlifts, and overhead presses. These multi-joint movements trigger robust testosterone responses while improving metabolic health markers associated with fertility.
Nutritional precision advances with macronutrient tracking, ensuring adequate protein intake (0.8-1g per pound of body weight) for tissue repair. Healthy fats comprise 25-30% of calories, supporting the synthesis of steroid hormones. Complex carbohydrates timed around workouts optimize energy availability without promoting insulin resistance.
Temperature regulation becomes a priority, avoiding hot tubs, saunas, and prolonged sitting that elevate scrotal temperature. Testicles hang externally, maintaining temperatures 2-4°C below core body temperature for optimal spermatogenesis. Loose-fitting underwear and frequent position changes during desk work preserve testicular thermoregulation.
Weeks six through eight introduce targeted supplementation beyond foundational multivitamins. Coenzyme Q10 (200-300mg daily) enhances mitochondrial function in sperm midpieces, improving motility. L-carnitine (2-3g daily) facilitates fatty acid metabolism for energy production. N-acetylcysteine supports glutathione synthesis, reinforcing antioxidant defenses.
Weeks 9-12: Optimization Phase
The final month consolidates established habits while addressing remaining lifestyle factors. Environmental toxin reduction focuses on eliminating plastics and replacing storage containers with glass alternatives. Phthalates and bisphenol-A leach from plastics, acting as endocrine disruptors that interfere with testosterone signaling and sperm development.
The organic produce selection prioritizes the “Dirty Dozen” fruits and vegetables with the highest pesticide residues. Organophosphate pesticides exhibit antiandrogenic effects and induce oxidative stress. Budget-conscious approaches focus organic spending on items consumed with edible skins, while conventional options suffice for produce with protective peels.
Advanced stress management incorporates weekly activities promoting relaxation and social connection. Chronic psychological stress elevates cortisol chronically, suppressing luteinizing hormone secretion necessary for testosterone production. Nature exposure, creative pursuits, and meaningful relationships buffer stress response systems.
Optimizing sexual activity frequency balances ejaculation intervals with maintaining sperm quality. Excessive abstinence beyond 7-10 days allows sperm aging in the epididymis, increasing DNA fragmentation. Conversely, daily ejaculation may reduce concentration in some individuals. Intervals of 2-4 days optimize most fertility parameters for conception attempts.
Final phase priorities:
- Eliminate endocrine-disrupting chemicals from the home environment
- Achieve 8-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Maintain exercise consistency without overtraining
- Continue comprehensive supplementation protocol
- Schedule follow-up semen analysis at day 90
- Prepare for ongoing maintenance habits beyond intervention
Exercise and Physical Activity Protocols
Optimal Training Frequency
Moderate-intensity exercise improves sperm quality through multiple physiological pathways, including enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity and improved hormonal profiles.
Research demonstrates that men exercising 150-300 minutes weekly exhibit superior semen parameters compared to sedentary counterparts.
However, excessive training volume and intensity paradoxically impair fertility by inducing oxidative stress and hypothalamic suppression.
Resistance training three times weekly stimulates testosterone production without inducing overtraining syndrome. Sessions lasting 45-60 minutes targeting major muscle groups provide sufficient stimulus for metabolic and hormonal benefits.
Progressive resistance ensures continued adaptation while avoiding staleness that accompanies excessive volume or frequency.
Cardiovascular Considerations
Aerobic exercise improves cardiovascular health and metabolic function, supporting reproductive capacity. Moderate-intensity activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for 30-40 minutes, 3-4 times weekly, enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammatory markers. These adaptations indirectly support spermatogenesis by optimizing the hormonal milieu.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) offers time-efficient alternatives for busy professionals. Sessions of 20-25 minutes incorporating work-to-rest ratios of 1:2 or 1:3 provide cardiovascular benefits without excessive oxidative stress. Limit HIIT sessions to 2-3 weekly, allowing adequate recovery between demanding efforts.
Excessive endurance training, particularly ultra-distance events or high-volume marathon preparation, may temporarily suppress reproductive function. Studies show elite endurance athletes sometimes exhibit reduced testosterone and impaired sperm parameters during peak training phases. Recreational fitness levels avoid these concerns while delivering health benefits.
Recovery and Adaptation
Rest days prove equally important as training sessions for physiological adaptation and hormone optimization. Growth hormone and testosterone secretion occur predominantly during deep sleep following a training stimulus. Inadequate recovery perpetuates cortisol elevation that antagonizes anabolic processes, including spermatogenesis.
Active recovery, incorporating gentle movement, stretching, or yoga, maintains blood flow without imposing additional training stress. These practices reduce muscle soreness while supporting parasympathetic nervous system activation. Foam rolling and mobility work address movement restrictions that may limit training effectiveness.
Movement Throughout the Day
Occupational sitting constitutes an independent risk factor for metabolic and reproductive dysfunction beyond discrete exercise sessions. Prolonged sitting elevates scrotal temperature and reduces overall energy expenditure. Implement standing desk intervals, walking meetings, and frequent position changes throughout the workday.
Target 8,000-10,000 steps daily through accumulated activities rather than relying solely on structured exercise. Park farther from destinations, take stairs instead of elevators, and incorporate walking calls or errands. Non-exercise activity thermogenesis contributes substantially to daily caloric expenditure and metabolic health.

Sleep Optimization and Circadian Biology
Sleep Duration Requirements
Testosterone production follows circadian rhythms, with peak secretion during nocturnal sleep, particularly during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Men sleeping fewer than six hours nightly exhibit testosterone levels 10-15% lower than those achieving seven to nine hours. This hormonal suppression directly affects spermatogenesis by reducing gonadotropin stimulation.
Sleep restriction also impairs glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, promoting inflammatory states incompatible with optimal reproductive function. Prioritize 7.5-9 hours of sleep opportunity nightly, recognizing individual variability in requirements. Consistent sleep schedules synchronize circadian oscillators governing reproductive hormones.
Sleep Architecture Quality
Sleep quality matters as much as duration, with deep, slow-wave sleep and REM cycles serving distinct physiological functions. Growth hormone secretion peaks during deep sleep, supporting tissue repair and anabolic processes. REM sleep facilitates neurological recovery and emotional regulation, affecting stress response systems.
Alcohol consumption, though sedating, fragments sleep architecture and reduces REM percentage. Even moderate evening drinking impairs sleep quality sufficiently to affect next-day hormonal profiles. Caffeine consumed within 8-10 hours of bedtime disrupts sleep initiation and architecture despite subjective sleepiness.
Environmental Optimization
The bedroom environment profoundly influences sleep quality through multiple sensory pathways. Temperature regulation between 65-68°F supports the natural decline in core body temperature necessary for sleep initiation. Warmer environments disrupt this thermoregulatory process, fragmenting sleep and reducing deep sleep percentages.
Complete darkness eliminates light exposure that suppresses melatonin secretion and disrupts circadian timing. Blackout curtains, eye masks, and the elimination of electronic displays preserve darkness. Blue light from screens proves particularly disruptive to circadian rhythms, warranting device cessation 1-2 hours before bedtime.
White noise machines or earplugs minimize acoustic disturbances that fragment sleep even without full awakening. Noise pollution increases stress hormone secretion and prevents progression through deeper sleep stages. Address environmental noise through soundproofing measures or masking technologies.
Circadian Rhythm Synchronization
Light exposure timing entrains circadian rhythms governing reproductive hormone secretion. Morning bright-light exposure, preferably natural sunlight, advances circadian phase and strengthens the rhythm’s amplitude. Spend 10-20 minutes outdoors within 30-60 minutes of waking to optimize circadian alignment.
Evening light exposure, particularly blue wavelengths, delays circadian timing and suppresses melatonin. Use blue-light-filtering apps on electronic devices, or wear blue-blocking glasses if evening screen use is unavoidable. Dim lighting after sunset supports a natural rise in melatonin and sleep preparation.
Meal timing serves as an additional circadian entrainment signal, with time-restricted feeding potentially strengthening metabolic rhythms. Aligning eating windows with daylight hours and avoiding late-night eating support circadian coherence. Consider a 12-14-hour overnight fasting interval to optimize metabolic and hormonal function.
Stress Management and Psychological Wellness
Stress Hormones and Fertility
Chronic stress elevation triggers sustained cortisol secretion, which directly suppresses hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) pulsatility. This disruption cascades through the reproductive axis, reducing luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone secretion, both of which are necessary for testicular function. Consequently, testosterone production and spermatogenesis both suffer under chronic stress conditions.
Psychological stress also increases the oxidative stress systemically, with reactive oxygen species accumulating in reproductive tissues. Lipid peroxidation damages sperm membranes while DNA strand breaks compromise genetic integrity. Stress management thus serves dual protective functions through hormonal and cellular mechanisms.
Evidence-Based Stress Reduction
Mindfulness meditation provides robust evidence for reducing cortisol levels and balancing the autonomic nervous system. Daily practice of 10-20 minutes activates parasympathetic pathways, countering stress-induced sympathetic dominance. Progressive muscle relaxation, body scanning, and breath-focused attention provide accessible entry points for meditation-naïve individuals.
Deep breathing exercises activate vagal tone, shifting autonomic balance toward parasympathetic predominance. Techniques like box breathing (4-second inhale, 4-second hold, 4-second exhale, 4-second hold) or extended exhalation (inhale 4 seconds, exhale 6-8 seconds) can rapidly reduce perceived stress. Practice during commutes, breaks, or before sleep for cumulative benefits.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques address thought patterns that perpetuate stress responses. Cognitive restructuring challenges distorted thinking, while behavioral activation increases engagement with rewarding activities. Professional guidance optimizes CBT implementation, while self-help resources provide valuable starting points for developing stress management skills.
Social Connection and Support
Strong social relationships buffer stress response systems through multiple pathways, including oxytocin release and reduced inflammatory cytokine production. Men with robust social networks exhibit lower cortisol levels and better overall health outcomes. Prioritize regular connection with friends, family, and community groups supporting emotional wellness.
Communication regarding fertility concerns with partners reduces psychological burden and strengthens relationship bonds. Shared understanding and mutual support transform fertility optimization from an individual obligation into a collaborative partnership. Consider couples counseling if fertility stress strains relationship quality.
Support groups, whether in-person or online, connect individuals facing similar challenges. Normalized experiences and the exchange of practical advice reduce isolation while providing accountability for lifestyle modifications. Fertility-focused communities offer a specialized understanding unavailable through general social networks.
Work-Life Balance Strategies
Occupational stress contributes substantially to overall stress burden, warranting boundary-setting and workload management. Communicate realistic capacity to supervisors and decline non-essential commitments during fertility optimization periods. Remote work options, flexible schedules, or compressed workweeks may reduce commute stress and increase recovery time.
Incorporate micro-breaks throughout workdays, stepping away from desks for brief walks or stretching. These interruptions reduce cumulative stress while addressing concerns about sedentary behavior. Use break time for genuine mental disengagement rather than screen-based activities, maintaining cognitive activation.
Vacation time provides extended recovery from chronic work stress, with complete disconnection from work communications proving essential. Plan restorative getaways emphasizing relaxation and enjoyable activities rather than exhausting travel itineraries. Regular vacations maintain stress resilience between fertility optimization efforts.
Environmental Toxin Reduction Strategies
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals
Phthalates, commonly found in plastics, personal care products, and fragrances, interfere with androgen receptor signaling and testosterone synthesis. These ubiquitous chemicals demonstrate anti-androgenic effects even at low exposure levels encountered through normal consumer product use. Replace plastic food storage with glass or stainless steel containers, avoiding microwaving plastic, which accelerates chemical leaching.
Bisphenol-A (BPA) and related compounds (BPS, BPF) in can linings and receipts exhibit estrogenic activity, disrupting hormonal balance. Choose fresh or frozen foods over canned alternatives when possible, declining receipt printing at point-of-sale transactions. BPA-free labels provide limited reassurance as substitute chemicals often demonstrate similar endocrine activity.
Parabens in cosmetics, shampoos, and lotions accumulate in tissues with potential reproductive effects. Read ingredient labels carefully and select paraben-free alternatives for daily-use products. Natural preservative systems using essential oils or vitamin E offer safer alternatives, though they require more frequent replacement.
Pesticide Exposure Reduction
Organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides demonstrate reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress induction and hormonal disruption. Agricultural workers face the highest exposures, though dietary intake contributes meaningfully to the general population burden. Prioritize organic produce for items consumed with edible skins: strawberries, spinach, apples, grapes, and tomatoes consistently rank highest in residue testing.
Home and garden pesticide use adds controllable sources of exposure. Integrated pest management using physical barriers, beneficial insects, and targeted spot treatments minimizes reliance on chemicals. Professional pest control services offering least-toxic approaches provide alternatives to conventional broadcast applications.
Heavy Metal Mitigation
Lead accumulation in bones leaches into circulation during physiological stress, interfering with sperm development. Older homes with lead paint or plumbing are primary sources of exposure. Water testing identifies lead contamination warranting filtration or plumbing replacement. Chelation therapy under medical supervision addresses documented elevated lead levels.
Mercury primarily enters the diet through large predatory fish that accumulate methylmercury through aquatic food chains. Limit consumption of tuna, swordfish, king mackerel, and shark, while emphasizing lower-mercury options like salmon, sardines, and anchovies. Dental amalgam removal requires specialized protocols to prevent acute exposure during extraction.
Cadmium from cigarette smoke represents the most significant exposure route for smokers. This toxic metal concentrates in the kidneys and reproductive organs, impairing fertility through multiple mechanisms. Smoking cessation eliminates the primary cadmium source while delivering numerous additional reproductive health benefits.
Household Product Choices
Conventional cleaning products release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contain reproductive toxicants. Green-certified alternatives made with plant-based ingredients minimize chemical exposure. Simple solutions like vinegar, baking soda, and castile soap address most household cleaning needs safely and economically.
Non-stick cookware coated with perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) releases toxic fumes when overheated. Cast iron, stainless steel, or ceramic alternatives provide durable cooking surfaces without the concerns about fluoropolymer contamination. Properly seasoned cast iron develops natural non-stick properties through use.
Flame retardants in furniture, electronics, and textiles accumulate in household dust, contributing to body burden through inhalation and ingestion. Choose products certified flame-retardant-free when replacing furniture or electronics. Regular wet-mopping and HEPA vacuum use reduce dust exposure.

Supplement Protocol Recommendations
Foundational Multivitamin
Comprehensive multivitamins provide nutritional insurance against dietary gaps that compromise spermatogenesis. Select formulations specifically designed for male fertility containing therapeutic doses of key nutrients rather than minimal RDA amounts. Look for methylated B-vitamins (methylfolate, methylcobalamin) offering superior bioavailability compared to synthetic folic acid and cyanocobalamin.
Timing matters for optimal absorption, with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) requiring consumption with dietary fats. Split dosing—half with breakfast, half with dinner—maintains steady nutrient levels while improving tolerability. Store supplements properly away from heat and light to preserve potency.
Targeted Antioxidant Support
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) concentrates in mitochondria-rich tissues, such as sperm midpieces, supporting energy production for motility. Ubiquinol represents the reduced, active form, demonstrating superior absorption compared to ubiquinone. Dosing ranges from 200-300mg daily, with effects accumulating over 12 weeks, matching spermatogenic cycles.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) provides cysteine for glutathione synthesis, the master intracellular antioxidant defending against oxidative damage. Clinical trials demonstrate improved sperm concentration, motility, and morphology with 600mg NAC daily. Take on an empty stomach for optimal absorption, though gastric sensitivity may necessitate food consumption.
Vitamin C ascorbate form (1000mg daily) and vitamin E as mixed tocopherols (400 IU daily) work synergistically to protect sperm membranes. These water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidants occupy different cellular compartments, providing comprehensive oxidative defense. Excessive vitamin E doses above 800 IU may paradoxically increase mortality risk, warranting moderate supplementation.
Amino Acid Formulations
L-carnitine transports fatty acids into mitochondria for beta-oxidation, fueling sperm motility through ATP generation. Acetyl-L-carnitine crosses membranes more readily, supporting both energetics and antioxidant functions. Combined supplementation of 2g L-carnitine with 1g acetyl-L-carnitine demonstrates superior results compared to either compound alone.
L-arginine serves as a nitric oxide precursor, improving blood flow to reproductive organs. Dosing of 3-5g daily enhances sperm concentration and motility in clinical studies. Divide doses throughout the day to minimize gastric discomfort, taking between meals for optimal absorption.
Herbal Adaptogens
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) demonstrates remarkable effects on stress reduction, testosterone production, and sperm parameters. Standardized extracts containing 5% withanolides at 600mg daily improve sperm concentration by 167% in one notable study. Effects accumulate over 90 days, aligning perfectly with spermatogenic timelines.
Tribulus terrestris may enhance luteinizing hormone secretion, indirectly supporting testosterone production. However, evidence remains mixed regarding efficacy in men without hypogonadism. Doses of 750-1500mg daily of standardized extracts appear safe, though benefits for fertility remain uncertain.
Maca root (Lepidium meyenii) demonstrates improved sperm concentration and motility in preliminary research. This Peruvian adaptogen may enhance sexual function independent of testosterone changes. Typical dosing ranges from 1.5-3g daily of gelatinized maca for improved digestibility.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) comprises up to 50% of sperm membrane fatty acids, underscoring the importance of adequate omega-3 status for normal sperm structure and function. Fish oil supplements providing 1-2g combined EPA and DHA daily improve morphology and membrane integrity. Choose molecularly distilled products that have been tested for heavy metal contamination.
Algae-based omega-3 supplements offer plant-based alternatives for vegetarians while avoiding exposure to marine toxins. DHA-focused algae oils support sperm health without EPA, though combined formulations provide broader anti-inflammatory benefits. Refrigerate after opening to prevent oxidation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see improvements in sperm quality?
Measurable improvements typically manifest after 90 days, corresponding to the complete spermatogenesis cycle from stem cell to mature spermatozoon. Some men notice enhanced sexual function and energy within 4-6 weeks as testosterone levels optimize.
However, maximal benefits require the full three-month intervention, allowing newly produced sperm incorporating lifestyle improvements to mature completely. Patience is essential, as premature semen analysis may reveal only minimal changes before the complete cohort replacement occurs.
Can stress alone cause poor sperm quality?
Chronic psychological stress significantly impairs sperm parameters through multiple mechanisms, including elevated cortisol, which suppresses reproductive hormones. Studies demonstrate that men under high stress exhibit reduced concentration and motility, and increased DNA fragmentation, compared to their relaxed counterparts.
Stress-induced oxidative damage affects developing sperm cells throughout the 90-day maturation window. However, stress rarely operates as the sole causative factor, typically interacting with nutritional deficiencies, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors in multifactorial patterns of fertility impairment.
Do laptops on the lap really damage sperm?
Laptop heat generation elevates scrotal temperature above the optimal range for spermatogenesis, which requires temperatures 2-4°C below core body temperature. Studies confirm that prolonged laptop use directly on the lap raises scrotal temperature sufficiently to impair sperm production temporarily.
Electromagnetic radiation from laptops may contribute additional detrimental effects beyond thermal damage. Place laptops on desks or use lap desks with cooling surfaces to prevent direct heat transfer to reproductive organs during extended work sessions.
Which exercises are best for sperm quality?
Moderate-intensity resistance training 3-4 times weekly optimizes testosterone production while avoiding overtraining-induced hormonal suppression. Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and presses stimulate robust hormonal responses supporting spermatogenesis.
Cardiovascular exercise at moderate intensity for 150-300 minutes weekly improves metabolic health without excessive oxidative stress. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, and cycling provide cardiovascular benefits supporting reproductive function. Avoid extreme endurance training, which may temporarily reduce testosterone and sperm parameters during peak training phases.
Are boxers or briefs better for fertility?
Loose-fitting boxers maintain lower scrotal temperatures compared to tight briefs, supporting optimal spermatogenesis. Studies demonstrate that men wearing boxer shorts exhibit 25% higher sperm concentration and 17% higher total sperm count than men wearing briefs.
Temperature regulation represents the primary mechanism, as constrictive underwear holds testicles closer to the body core, elevating temperature. Choose breathable natural fabrics like cotton over synthetic materials that trap additional heat due to reduced air circulation.
Can varicoceles be fixed without surgery?
Varicoceles—enlarged veins in the scrotum—elevate testicular temperature and increase oxidative stress, impairing sperm quality in many affected men. Conservative management, including scrotal support, anti-inflammatory supplements, and antioxidants, provides modest benefits but does not address the underlying vascular abnormality.
Surgical varicocelectomy or percutaneous embolization effectively eliminates varicoceles, with 60-70% of men experiencing improved sperm parameters post-intervention. Consult a reproductive urologist to discuss treatment necessity based on varicocele grade, symptoms, and degree of fertility impairment demonstrated through semen analysis.
How much alcohol is safe when trying to conceive?
Alcohol metabolism generates acetaldehyde and reactive oxygen species, directly damaging developing sperm DNA. Even moderate consumption of 2-3 drinks per day results in measurable reductions in sperm concentration and motility.
Conservative recommendations suggest limiting intake to 3-4 drinks weekly maximum during active fertility optimization efforts. Complete abstinence eliminates alcohol-related reproductive toxicity entirely, representing the safest approach for men with existing sperm quality concerns or couples experiencing conception difficulties.
Do hot showers affect sperm production?
Brief hot showers typically don’t elevate scrotal temperature sufficiently or long enough to significantly impact spermatogenesis. However, prolonged exposure to hot water, particularly baths exceeding 102°F for 30+ minutes, raises testicular temperature above optimal ranges.
Hot tubs and saunas pose greater concerns due to higher temperatures and longer typical exposure durations. Men actively optimizing fertility should avoid hot tubs, limit sauna use to occasional brief sessions, and prefer warm rather than excessively hot showers.
Can cell phone radiation damage sperm?
Radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation from cell phones has the potential to cause reproductive effects through both thermal and non-thermal mechanisms. Studies show that men who carry phones in their front pockets exhibit reduced motility and viability compared to those who store their phones elsewhere.
Mechanisms include electromagnetic field disruption of cellular processes and the generation of low-grade heat affecting nearby testicular tissue. Minimize exposure by using speaker phone, keeping devices in bags or back pockets, and avoiding prolonged phone placement near reproductive organs during use or charging.
When should I see a fertility specialist?
Couples unable to conceive after 12 months of regular unprotected intercourse warrant fertility evaluation for both partners. Men over 40 or with known risk factors should seek assessment after 6 months.
Semen analysis provides an initial evaluation of male fertility potential, assessing concentration, motility, morphology, and volume. Based on results, reproductive urologists or fertility specialists determine whether additional testing or treatments like varicocele repair, hormonal therapy, or assisted reproductive technologies are indicated.
Maintaining Long-Term Fertility Health
Sustaining improvements achieved during the 90-day intervention requires lifestyle integration rather than temporary compliance. Habits established during the protocol become permanent practices supporting lifelong reproductive and general health. View fertility optimization as a gateway to comprehensive wellness rather than an isolated goal.
Periodic semen analysis every 6-12 months monitors parameter stability and identifies emerging concerns before significantly impacting fertility potential. Baseline measurements established during optimization provide reference points for longitudinal tracking. Many factors influence semen parameters, so single analyses shouldn’t trigger excessive concern without confirming trends through repeat testing.
Continue foundational supplements, including multivitamin, omega-3, and antioxidant support, indefinitely. These nutrients address ongoing oxidative stress and nutritional gaps that persist despite optimal dietary habits. Adjust herbal adaptogens cyclically, taking periodic breaks to prevent tolerance development while reassessing need based on stress levels and general wellbeing.
The weekly habit structure provides a sustainable framework applicable beyond fertility goals. Consistent sleep schedules, regular exercise, stress management practices, and whole food nutrition support longevity, disease prevention, and quality of life across the lifespan. Reproductive health serves as a sensitive barometer for overall wellness, making fertility optimization efforts beneficial regardless of conception timing.
Schedule annual physical examinations, including testosterone levels, metabolic panels, and cardiovascular markers. These screenings identify developing health concerns before symptoms manifest, allowing early intervention. Discuss fertility history with healthcare providers, as reproductive function predicts future health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and mortality risk.
Build support systems reinforcing healthy habits through accountability and social connection. Whether workout partners, meal prep groups, or online communities, shared commitment increases the likelihood of adherence. Celebrate milestones and progress while maintaining perspective amid the inherent setbacks of behavior change processes.
Adapt protocols as life circumstances evolve, recognizing flexibility prevents all-or-nothing thinking that sabotages long-term success. Travel, career demands, and family obligations require accommodation without abandoning core principles. Return to foundational practices during stable periods while implementing modified approaches during challenging times.
Continue learning about reproductive health and fertility research, staying informed about emerging evidence. Scientific understanding evolves, with new interventions and refined recommendations appearing regularly. Critical evaluation of health information sources prevents misinformation while identifying valuable innovations worth implementing.
The 90-day transformation provides momentum for sustained wellness investment. Improved energy, sexual function, body composition, and psychological well-being reinforce commitment beyond fertility motivation. These holistic benefits demonstrate that reproductive optimization enhances overall quality of life, making continued adherence intrinsically rewarding rather than an obligation.
Consider this protocol the beginning, rather than the endpoint, of the health optimization journey. Skills developed—nutritional awareness, stress management, exercise programming—transfer to infinite applications supporting thriving across domains. Fertility serves as a catalyst for positive change, rippling through all life areas and transforming health trajectories long after conception goals are achieved.
Ready to transform your reproductive health? Explore our comprehensive guides on testosterone optimization, nutritional strategies for male wellness, and advanced fertility treatments. Your journey to optimal vitality begins with informed action—discover additional resources supporting your health goals today.

