You just celebrated your 35th birthday, but what if your body was actually aging like a 45-year-old—or thriving like a 25-year-old? Biological age testing has revolutionized how we understand aging, revealing that the number of candles on your cake doesn’t tell the whole story. While chronological age simply tracks the years you’ve been alive, your biological age measures how well your cells, tissues, and organs are actually functioning.
Scientists now use cutting-edge tools like epigenetic clocks and DNA methylation analysis to measure biological aging with remarkable accuracy. The exciting news? Unlike your chronological age, which marches forward relentlessly, you can actually slow down—or even reverse—your biological age through targeted lifestyle changes.
What Is Biological Age?
Understanding Age Beyond Numbers
Biological age reflects the functional health of your body at the cellular level. Two people born on the same day can have vastly different biological ages depending on genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures.
Think of chronological age as the manufacturing date on your car, while biological age is the actual mileage and condition of the engine. Your body’s “mileage” depends on factors like oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA damage, and cellular repair mechanisms.
The Science Behind Aging
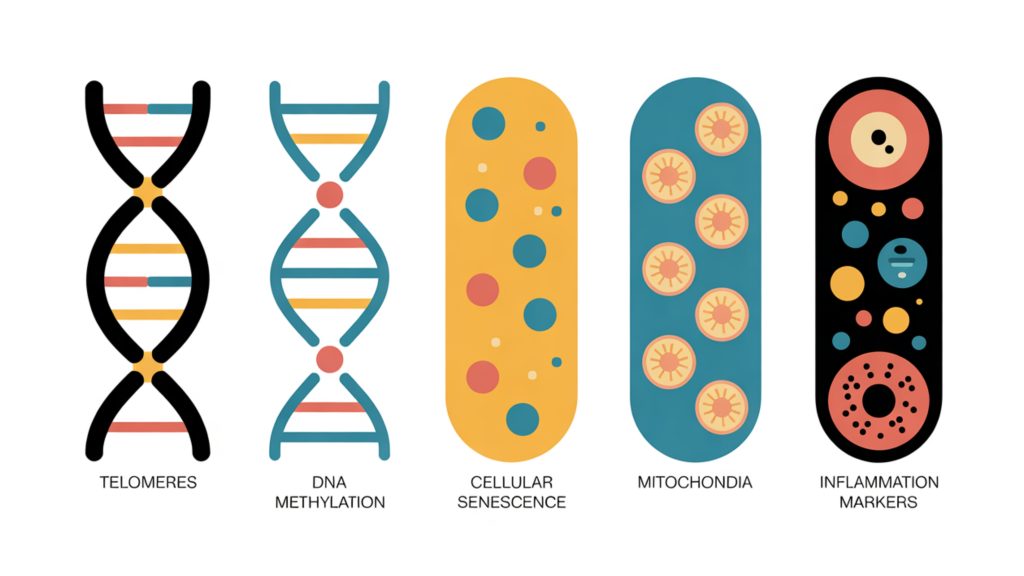
Aging involves multiple interconnected processes:
- Cellular senescence – when cells stop dividing and become dysfunctional
- Telomere shortening – protective DNA caps that shrink with each cell division
- Epigenetic alterations – chemical modifications to DNA that change gene expression
- Mitochondrial dysfunction – energy-producing cellular powerhouses decline
- Chronic inflammation – persistent low-level immune activation
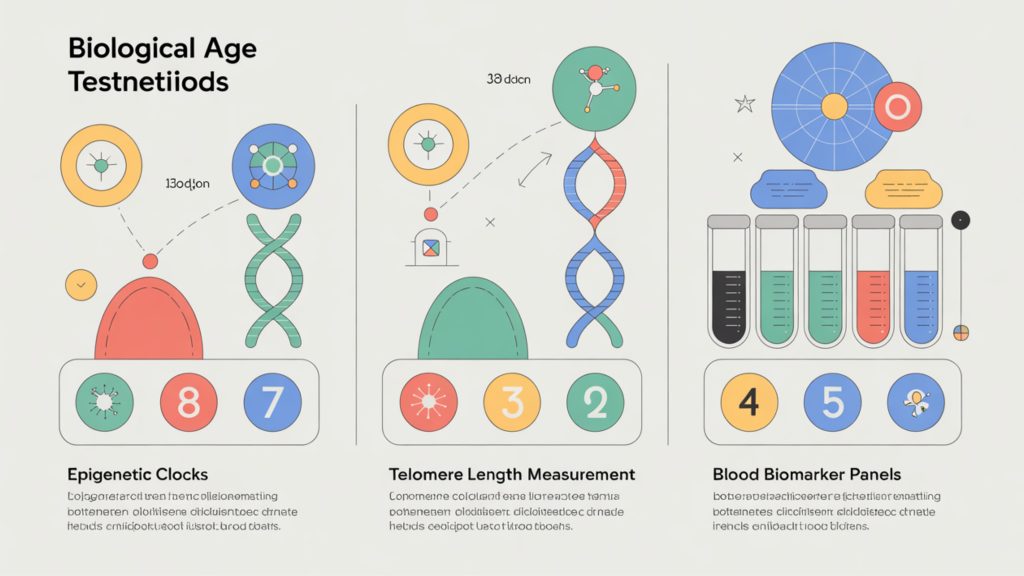
How Biological Age Is Measured
Epigenetic Clocks: The Gold Standard
Epigenetic clocks analyze DNA methylation patterns—chemical tags on your DNA that change predictably with age. The most widely used models include:
Horvath Clock – Developed by UCLA researcher Steve Horvath, this measures methylation at 353 specific DNA sites and works across multiple tissue types.
Hannum Clock – Uses 71 methylation markers specifically from blood samples.
GrimAge – Predicts mortality risk and disease outcomes more accurately than other clocks, incorporating markers for cardiovascular health and inflammation.
EpiAge – A newer 2025 model using just three DNA methylation sites in the ELOVL2 gene, making testing simpler and more accessible.
Recent 2025 research introduced EpInflammAge, combining epigenetic and inflammatory markers with an impressive accuracy of 7 years mean error.
Telomere Length Testing
Telomeres are protective caps at the end of chromosomes that shorten each time cells divide. While telomere length provides insights into cumulative cellular aging, recent research shows it’s less predictive of overall biological age than epigenetic clocks.
Testing methods include:
- qPCR – Fast and affordable but less precise
- Flow-FISH – Measures individual cells but requires specialized equipment
- TRF Analysis – Most accurate but complex and expensive
Blood-Based Biomarkers
Comprehensive biological age assessments also examine:
- Inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, cytokines)
- Metabolic indicators (fasting glucose, insulin sensitivity)
- Lipid profiles (ApoB, triglycerides)
- Hormonal levels
- Oxidative stress markers
Consumer Testing Kits: Worth It?
At-Home Test Accuracy
The biological age testing market exploded in 2024-2025, with companies offering direct-to-consumer kits. However, accuracy varies significantly between providers.
High-Quality Options:
- SystemAge reports 99% accuracy across 1,600 validation cases
- TruDiagnostic offers comprehensive reports but with lower accuracy around 58%
- HealthTAV provides clinical-grade telomere analysis
Important Limitations
A 2025 critical analysis found that while biological age testing shows promise, it “currently lacks the reliability needed for widespread clinical use”. Key concerns include:
- Methodological variability between tests
- Lack of standardization across companies
- Ethnic and population diversity affecting accuracy
- Cost versus actionable insights ratio
When one researcher tested four different biological age kits simultaneously, results varied significantly, raising questions about precision.
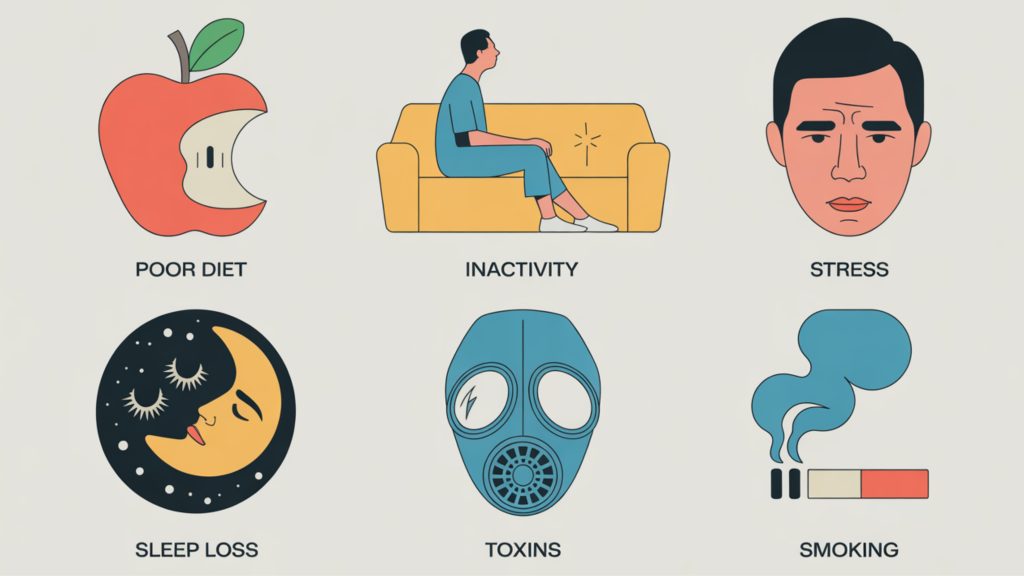
What Accelerates Biological Aging
Lifestyle Factors That Age You
Research consistently identifies these aging accelerators:
Poor Diet – Excessive added sugar, processed foods, and inflammatory seed oils damage cellular function. Studies show that consuming 10 extra grams of added sugar daily can age you by 2.4 months.
Sedentary Behavior – Physical inactivity correlates with shorter telomeres and accelerated epigenetic aging.
Chronic Stress – Elevated cortisol levels trigger inflammatory cascades and DNA damage.
Sleep Deprivation – Less than 7 hours nightly impairs cellular repair mechanisms.
Smoking and Excessive Alcohol – Directly damage DNA and accelerate telomere shortening.
Environmental Exposures
External factors that increase biological age include:
- Air pollution and environmental toxins
- Chronic sun exposure without protection
- Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (plastics, pesticides)
- Electromagnetic radiation exposure
How to Reduce Your Biological Age
Evidence-Based Interventions
A groundbreaking 2025 study demonstrated that lifestyle interventions could reverse biological age by an average of 5 years in just 8 weeks.
Nutrition Strategies
Eat These Daily:
- 2 cups dark leafy greens (kale, spinach, Swiss chard)
- 2 cups cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
- 3 cups colorful vegetables (peppers, carrots, beets)
- ¼ cup each pumpkin and sunflower seeds
- Methylation adaptogens: ½ cup berries, 2 garlic cloves, green tea
Avoid:
- Added sugars and refined carbohydrates
- Processed meats and trans fats
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Exercise Protocols
Physical activity powerfully impacts biological aging. Research from 2025 found that individuals with above-average cardiorespiratory fitness (VO2max in 70th percentile or higher) possessed significantly longer telomeres than sedentary peers.
Weekly Exercise Goals:
- 150 minutes moderate-to-vigorous cardio
- 90 minutes strength training (can reduce biological age by nearly 4 years)
- 2 days flexibility work (yoga, stretching)
- Daily movement breaks if desk-bound
Sleep Optimization
Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Sleep is when your body performs critical cellular repair, clears metabolic waste from the brain, and regulates hormones.
Sleep Hygiene Tips:
- Maintain consistent sleep/wake times
- Create a cool, dark sleeping environment
- Avoid screens 60 minutes before bed
- Practice relaxation breathing exercises
Stress Management
The study participants who reversed their biological age practiced breathing exercises twice daily. Chronic stress significantly impacts cellular aging through cortisol elevation and inflammatory pathways.
Proven Techniques:
- Mindfulness meditation (10-20 minutes daily)
- Deep breathing exercises (4-7-8 method)
- Regular social connections
- Time in nature
The Future of Biological Age Testing
Emerging Technologies
The field is rapidly evolving with innovations expected through 2026:
AI-Powered Analysis – Machine learning models now integrate multiple aging biomarkers for more accurate predictions.
Simplified Testing – New methods like EpiAge require analyzing just 3 DNA sites instead of hundreds, making testing more accessible and affordable.
Organ-Specific Clocks – Researchers are developing tissue-specific biological age tests for brain, heart, liver, and other organs.
Predictive Health Applications – Biological age testing is being validated for predicting IVF success, cardiovascular disease risk, and neurodegenerative conditions.
Clinical Integration
Major health systems are beginning to incorporate biological age assessment into preventative medicine protocols. The 2025 Osaka-Kansai Expo featured biological aging measurement as a cornerstone of future healthcare.
FAQs About Biological vs. Chronological Age
Q: Can my biological age be younger than my chronological age?
Yes, absolutely. Biological age reflects your cellular health, not the years you’ve been alive. Research shows that people with healthy lifestyles, regular exercise, nutritious diets, and good stress management often have biological ages 5-10 years younger than their chronological age. The key is consistent healthy habits that protect your cells from damage and support repair mechanisms.
Q: How accurate are at-home biological age tests?
Accuracy varies significantly between companies and testing methods. Clinical-grade tests like SystemAge report 99% accuracy, while others show accuracy around 58%. The biggest limitation is that testing standards aren’t yet unified across the industry. If you’re considering testing, research the specific company’s validation studies and understand that results should be viewed as estimates rather than precise measurements.
Q: What’s the difference between epigenetic clocks and telomere tests?
Epigenetic clocks measure chemical modifications (methylation patterns) on your DNA that change predictably with age, analyzing anywhere from 3 to 353 specific sites. Telomere tests measure the length of protective DNA caps at chromosome ends that shorten with cell division. Research indicates epigenetic clocks are better predictors of disease risk and mortality than telomere length alone. Most comprehensive biological age assessments now use epigenetic clocks as the primary tool.
Q: How quickly can I reverse my biological age?
Research demonstrates measurable changes can occur surprisingly fast. A landmark 2025 study showed participants reversed their biological age by an average of 5 years in just 8 weeks through intensive lifestyle interventions. However, sustainable changes typically take 3-6 months of consistent healthy habits. The key factors include eating nutrient-dense whole foods, exercising 150+ minutes weekly, sleeping 7-9 hours nightly, and managing stress through meditation or breathing exercises.
Q: Does biological age testing predict how long I’ll live?
Biological age is a better predictor of mortality risk than chronological age, but it’s not a crystal ball. The GrimAge epigenetic clock shows the strongest association with all-cause mortality among current testing methods. However, biological age should be viewed as a modifiable risk factor—like blood pressure or cholesterol—rather than a fixed destiny. The real value is identifying areas for improvement and tracking whether interventions are working.
Q: Are biological age tests covered by insurance?
Currently, most biological age tests are not covered by standard health insurance as they’re considered preventative or “wellness” testing rather than diagnostic. Costs range from $75 for basic telomere tests to $500+ for comprehensive epigenetic clock analyses. Some health savings accounts (HSAs) or flexible spending accounts (FSAs) may cover these tests, but policies vary. As the science becomes more established, insurance coverage may expand.
Q: What’s the Horvath Clock everyone talks about?
The Horvath Clock is the original epigenetic clock developed by UCLA scientist Steve Horvath in 2013. It analyzes DNA methylation patterns at 353 specific sites to estimate biological age with remarkable accuracy—typically within 3-4 years. What makes it revolutionary is that it works across multiple tissue types (blood, skin, brain, organs), suggesting it measures a fundamental aging process. The Horvath Clock has become the foundation for many subsequent aging research studies.
Q: Can stress really age me faster at the cellular level?
Yes, chronic stress demonstrably accelerates biological aging through multiple mechanisms. Elevated cortisol triggers inflammatory responses, damages telomeres, and alters DNA methylation patterns. A 2025 study found that mothers with higher marital satisfaction had 4-fold greater likelihood of telomere lengthening, while negative social interactions accelerated telomere shortening. The good news is that stress management interventions—like daily breathing exercises and mindfulness—can reverse these effects.
Q: Is biological age testing useful for young adults in their 20s and 30s?
Absolutely. While biological age testing has historically focused on older populations, establishing a baseline in your 20s or 30s provides valuable information for preventative health strategies. Young adults can identify whether lifestyle factors (poor sleep, high stress, poor diet) are already accelerating aging, allowing for early course correction. Recent 2025 research specifically developed epigenetic clocks optimized for adolescents and young adults to improve accuracy in this age group.
Q: Do genetics determine my biological age or can lifestyle override them?
Genetics influence only 15-25% of aging outcomes. The remaining 75-85% is determined by lifestyle, environment, and behaviors—factors you can control. This is encouraging news: even if you have genetic predispositions to certain conditions, healthy lifestyle choices can significantly slow biological aging. Studies consistently show that exercise, nutrition, sleep, and stress management powerfully impact biological age regardless of genetic background.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between biological and chronological age empowers you to take control of your health trajectory. While you can’t stop chronological time, emerging science proves you can slow—and even reverse—cellular aging through evidence-based lifestyle modifications.
The eight-week intervention study demonstrates that combining nutrient-dense nutrition, regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management can reverse biological age by five years. These aren’t genetic lottery winners or biohacking billionaires—they’re ordinary people who committed to sustainable healthy habits.
Whether you choose to invest in biological age testing or simply implement the proven strategies outlined here, remember that small daily choices compound over time. Your biological age is a dynamic, modifiable indicator of health—not a fixed destiny.
Explore more evidence-based nutrition guides to optimize your health and wellness on the Healthy Living page.

